Fittings for Threaded Pipe systems
Definition and Details of Threaded Fittings ASME B16.11
Threaded joints, perhaps one of the earliest methods for connecting piping systems, find their primary application in small pipe diameters, often referred to as small bore piping, typically encompassing pipes with a nominal diameter of NPS 2 or smaller.
The ASME B1.20.1 standard serves as the definitive source for dimensional specifications pertaining to taper pipe threads. This comprehensive document provides essential details, including the number of threads per inch, pitch diameter, and normal engagement lengths for all pipe diameters.
Threaded piping is most commonly employed in cost-effective, noncritical scenarios, including domestic water supply, fire protection systems, and industrial cooling water networks.
Threaded fittings are typically crafted from materials such as cast gray or malleable iron, cast brass or bronze, as well as forged alloys and carbon steel. These fittings are accessible in three distinct pressure ratings: Class 2000, 3000, and 6000.
NPT Thread
Every fitting featured on this page is equipped with NPT threads conforming to ASME B1.20.1 standards. NPT, short for the American National Pipe Thread Tapered, stands as the most renowned and extensively utilized connection method, serving as both the mechanical joint and hydraulic seal. NPT threads feature a tapered male and female thread design, creating a seal when paired with Teflon® tape or jointing compound.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Threaded Fittings
Advantages
- Installation productivity is reasonably elevated, with only moderate demands for specialized installation skills.
- Leakage integrity is commendable in low-pressure, low-temperature installations that do not experience significant vibration.
Disadvantages
- Sudden temperature fluctuations can induce leaks by causing differential thermal expansion disparities between the pipe and fittings.
- Vibration has the potential to trigger fatigue failures in threaded pipe joints, primarily due to the heightened stress concentration at the sharp notches found at the thread base.
- In hazardous piping systems, it is advisable to steer clear of threaded connections whenever feasible. They exhibit notable susceptibility to fatigue damage, particularly in cases where exposed threads are susceptible to corrosion.
Product Range
PRODUCT:
ELBOW 90 & 45 DEG., EQUAL & UNEQUAL TEE, CONCENTRIC & ECCENTRIC REDUCER, CAP, UNION, SOCKET, STUB END, SWAGE NIPPLE, FULL & HALF COUPLING, WELDOLET, THREADOLET, ELBOWLET, SOCKOLET, C ROSS
SIZE:
FROM 3/4″ NB TO 4″ NB.
CLASS:
FROM 2000# TO 9000#.
DIMENSION:
ASME / ANSI B16.11
MATERIAL:
CARBON STEEL GRADE-A105, COPPER NICKLE 90/10, 70/30
STAINLESS STEEL GRADE – A182 F304/L, 304H, 316/L, 316H, 321 ETC.
ALLOY STEEL GRADE – A182 F1, 5, 9, 11, F22, LF2 ETC.
COPPER NICKLE GRADE 90/10, 70/30.
HIGH TENSILE GRADES – WPHY F52, 60, 65, 70 ETC.
STAINLESS STEEL GRADE – A182 F304/L, 304H, 316/L, 316H, 321 ETC.
ALLOY STEEL GRADE – A182 F1, 5, 9, 11, F22, LF2 ETC.
COPPER NICKLE GRADE 90/10, 70/30.
HIGH TENSILE GRADES – WPHY F52, 60, 65, 70 ETC.
Dimensions
Elbow 90°
Tee
Cross
Elbow 45°
Full-coupling
Cap (End Cap)
Square head plug
Hex head plug
Round head plug
Hex head bushing
Union (MSS SP-83)
Elbow 90°
Dimensions Threaded Elbows
90°/45° ASME B16.11
Class 2000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 33 | 3.18 | 28 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 38 | 3.18 | 33 | 25 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 46 | 3.68 | 38 | 28 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 56 | 3.89 | 44 | 33 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 62 | 4.01 | 51 | 35 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 75 | 4.27 | 60 | 43 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 92 | 5.61 | 76 | 52 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 109 | 5.99 | 86 | 64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 146 | 6.55 | 106 | 79 |
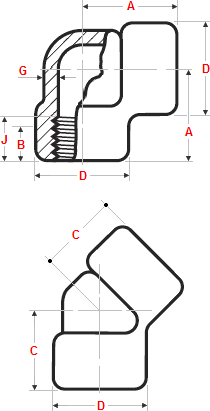
Class 3000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 38 | 4.09 | 33 | 25 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 46 | 4.32 | 38 | 28 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 56 | 4.98 | 44 | 33 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 62 | 5.28 | 51 | 35 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 75 | 5.56 | 60 | 43 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 84 | 7.14 | 64 | 44 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 102 | 7.65 | 83 | 52 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 121 | 8.84 | 95 | 64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 11.18 | 114 | 79 |

Class 6000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 46 | 8.15 | 38 | 28 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 56 | 8.53 | 44 | 33 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 62 | 9.93 | 51 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 75 | 10.59 | 60 | 43 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 84 | 11.07 | 64 | 44 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 102 | 12.09 | 83 | 52 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 121 | 15.29 | 95 | 64 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 146 | 16.64 | 106 | 79 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 18.67 | 114 | 79 |

General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
Tee
Dimensions Threaded Tees & Crosses
ASME B16.11
Class 2000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 33 | 28 | 3.18 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 38 | 33 | 3.18 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 46 | 38 | 3.68 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 56 | 44 | 3.89 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 62 | 51 | 4.01 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 75 | 60 | 4.27 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 92 | 76 | 5.61 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 109 | 86 | 5.99 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 146 | 106 | 6.55 |
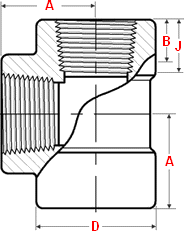
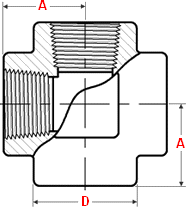
Class 3000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 38 | 33 | 4.09 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 46 | 38 | 4.32 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 56 | 44 | 4.98 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 62 | 51 | 5.28 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 75 | 60 | 5.56 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 84 | 64 | 7.14 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 102 | 83 | 7.65 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 121 | 95 | 8.84 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 114 | 11.18 |


Class 6000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 46 | 38 | 8.15 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 56 | 44 | 8.53 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 62 | 51 | 9.93 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 75 | 60 | 10.59 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 84 | 64 | 11.07 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 102 | 83 | 12.09 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 121 | 95 | 15.29 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 146 | 106 | 16.64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 114 | 18.67 |


General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
Cross
Dimensions Threaded Tees & Crosses
ASME B16.11
Class 2000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 33 | 28 | 3.18 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 38 | 33 | 3.18 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 46 | 38 | 3.68 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 56 | 44 | 3.89 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 62 | 51 | 4.01 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 75 | 60 | 4.27 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 92 | 76 | 5.61 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 109 | 86 | 5.99 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 146 | 106 | 6.55 |


Class 3000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 38 | 33 | 4.09 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 46 | 38 | 4.32 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 56 | 44 | 4.98 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 62 | 51 | 5.28 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 75 | 60 | 5.56 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 84 | 64 | 7.14 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 102 | 83 | 7.65 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 121 | 95 | 8.84 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 114 | 11.18 |


Class 6000 |
|||||
| NPS | Min Length of Thread | Outside Dia of Band D |
Center to End A |
Min WT |
|
| B | J | ||||
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 46 | 38 | 8.15 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 56 | 44 | 8.53 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 62 | 51 | 9.93 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 75 | 60 | 10.59 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 84 | 64 | 11.07 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 102 | 83 | 12.09 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 121 | 95 | 15.29 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 146 | 106 | 16.64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 114 | 18.67 |


General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
Elbow 45°
Dimensions Threaded Elbows
90°/45° ASME B16.11
Class 2000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 33 | 3.18 | 28 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 38 | 3.18 | 33 | 25 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 46 | 3.68 | 38 | 28 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 56 | 3.89 | 44 | 33 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 62 | 4.01 | 51 | 35 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 75 | 4.27 | 60 | 43 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 92 | 5.61 | 76 | 52 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 109 | 5.99 | 86 | 64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 146 | 6.55 | 106 | 79 |

Class 3000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 38 | 4.09 | 33 | 25 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 46 | 4.32 | 38 | 28 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 56 | 4.98 | 44 | 33 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 62 | 5.28 | 51 | 35 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 75 | 5.56 | 60 | 43 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 84 | 7.14 | 64 | 44 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 102 | 7.65 | 83 | 52 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 121 | 8.84 | 95 | 64 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 11.18 | 114 | 79 |

Class 6000 |
||||||
| NPS | Min Thread Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Center to End | ||
| B | J | D | G | 90° A |
45° C |
|
| 1/2 | 10.9 | 13.6 | 46 | 8.15 | 38 | 28 |
| 3/4 | 12.7 | 13.9 | 56 | 8.53 | 44 | 33 |
| 1 | 14.7 | 17.3 | 62 | 9.93 | 51 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 17 | 18 | 75 | 10.59 | 60 | 43 |
| 1.1/2 | 17.8 | 18.4 | 84 | 11.07 | 64 | 44 |
| 2 | 19 | 19.2 | 102 | 12.09 | 83 | 52 |
| 2.1/2 | 23.6 | 28.9 | 121 | 15.29 | 95 | 64 |
| 3 | 25.9 | 30.5 | 146 | 16.64 | 106 | 79 |
| 4 | 27.7 | 33 | 152 | 18.67 | 114 | 79 |

General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
Full-coupling
Dimensions Threaded Full and Half Couplings
ASME B16.11
Class 3000 |
||||
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min Thread Length | |
| A | D | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 48 | 28 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 51 | 35 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 60 | 44 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 67 | 57 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 79 | 64 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 86 | 76 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 92 | 92 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 108 | 108 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 121 | 140 | 27.7 | 33 |
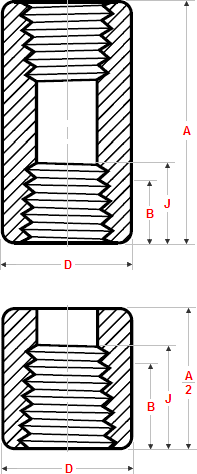
Class 6000 |
||||
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min Thread Length | |
| A | D | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 48 | 38 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 51 | 44 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 60 | 57 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 67 | 64 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 79 | 76 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 86 | 92 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 92 | 108 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 108 | 127 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 121 | 159 | 27.7 | 33 |

General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
Cap (End Cap)
Dimensions Threaded End Caps
ASME B16.11
Class 3000 |
|||||
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Min Thread Length | |
| A | D | G | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 32 | 28 | 6.4 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 37 | 35. | 6.4 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 41 | 44 | 9.7 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 44 | 57 | 9.7 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 44 | 64 | 11.2 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 48 | 76 | 12.7 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 60 | 92 | 15.7 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 65 | 108 | 19 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 68 | 140 | 22.4 | 27.7 | 33 |
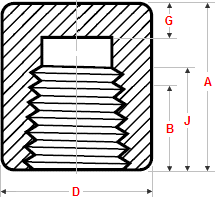

Class 6000 |
|||||
| NPS | Length | Outside Dia | Min WT | Min Thread Length | |
| A | D | G | B | J | |
| 1/2 | 33 | 38 | 7.9 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 3/4 | 38 | 44 | 7.9 | 12.7 | 13.9 |
| 1 | 43 | 57 | 11.2 | 14.7 | 17.3 |
| 1.1/4 | 46 | 64 | 11.2 | 17 | 18 |
| 1.1/2 | 48 | 76 | 12.7 | 17.8 | 18.4 |
| 2 | 51 | 92 | 15.7 | 19 | 19.2 |
| 2.1/2 | 64 | 108 | 19 | 23.6 | 28.9 |
| 3 | 68 | 127 | 22.4 | 25.9 | 30.5 |
| 4 | 75 | 159 | 28.4 | 27.7 | 33 |


General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Dimension (B) is minimum length of perfect thread.
The length of useful thread (B plus threads with fully formed roots and flat crests) shall not be less than J.
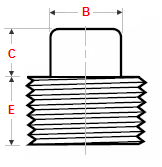
Square head plug
Dimensions Hex & Square & Round Head Plugs
ASME B16.11

Hex head plug

Square head plug

Round head plug
Hex Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Hex Height J |
Nominal F |
| 1/2 | 14 | 8 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 10 | 27 |
| 1 | 19 | 10 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 44.5 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 51 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 63.5 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 76 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 89 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 117.5 |
Square Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Square Height C |
Min Width Flats B |
| 1/2 | 14 | 10 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 11 | 16 |
| 1 | 19 | 13 | 21 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 24 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 28 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 32 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 36 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 41 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 65 |
Round Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length A |
Nominal Head Dia D |
Min Length E |
| 1/2 | 44 | 21 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 44 | 27 | 16 |
| 1 | 51 | 33 | 19 |
| 1.1/4 | 51 | 43 | 21 |
| 1.1/2 | 51 | 48 | 21 |
| 2 | 64 | 60 | 22 |
| 2.1/2 | 70 | 73 | 37 |
| 3 | 70 | 89 | 28 |
| 4 | 76 | 114 | 32 |
General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
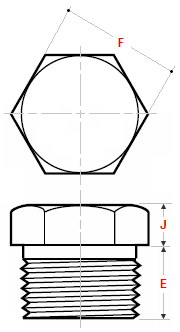
Hex head plug
Dimensions Hex & Square & Round Head Plugs
ASME B16.11

Hex head plug

Square head plug

Round head plug
Hex Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Hex Height J |
Nominal F |
| 1/2 | 14 | 8 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 10 | 27 |
| 1 | 19 | 10 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 44.5 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 51 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 63.5 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 76 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 89 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 117.5 |

Square Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Square Height C |
Min Width Flats B |
| 1/2 | 14 | 10 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 11 | 16 |
| 1 | 19 | 13 | 21 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 24 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 28 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 32 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 36 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 41 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 65 |

Round Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length A |
Nominal Head Dia D |
Min Length E |
| 1/2 | 44 | 21 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 44 | 27 | 16 |
| 1 | 51 | 33 | 19 |
| 1.1/4 | 51 | 43 | 21 |
| 1.1/2 | 51 | 48 | 21 |
| 2 | 64 | 60 | 22 |
| 2.1/2 | 70 | 73 | 37 |
| 3 | 70 | 89 | 28 |
| 4 | 76 | 114 | 32 |

General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
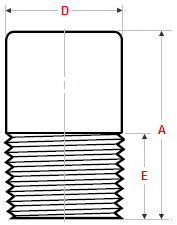
Round head plug
Dimensions Hex & Square & Round Head Plugs
ASME B16.11

Hex head plug

Square head plug

Round head plug
Hex Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Hex Height J |
Nominal F |
| 1/2 | 14 | 8 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 10 | 27 |
| 1 | 19 | 10 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 44.5 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 51 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 63.5 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 76 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 89 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 117.5 |

Square Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Square Height C |
Min Width Flats B |
| 1/2 | 14 | 10 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 11 | 16 |
| 1 | 19 | 13 | 21 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 14 | 24 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 16 | 28 |
| 2 | 22 | 18 | 32 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 19 | 36 |
| 3 | 28 | 21 | 41 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 | 65 |

Round Head Plug |
|||
| NPS | Min Length A |
Nominal Head Dia D |
Min Length E |
| 1/2 | 44 | 21 | 14 |
| 3/4 | 44 | 27 | 16 |
| 1 | 51 | 33 | 19 |
| 1.1/4 | 51 | 43 | 21 |
| 1.1/2 | 51 | 48 | 21 |
| 2 | 64 | 60 | 22 |
| 2.1/2 | 70 | 73 | 37 |
| 3 | 70 | 89 | 28 |
| 4 | 76 | 114 | 32 |

General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
Hex head bushing
Dimensions Hex Head Bushings
ASME B16.11
| NPS | Min Length E |
Min Hex Height C |
Nominal F |
| 1/2 | 14 | 5 | 22 |
| 3/4 | 16 | 6 | 27 |
| 1 | 19 | 6 | 35 |
| 1.1/4 | 21 | 7 | 44.5 |
| 1.1/2 | 21 | 8 | 51 |
| 2 | 22 | 9 | 63.5 |
| 2.1/2 | 27 | 10 | 76 |
| 3 | 28 | 10 | 89 |
| 4 | 32 | 13 | 117.5 |
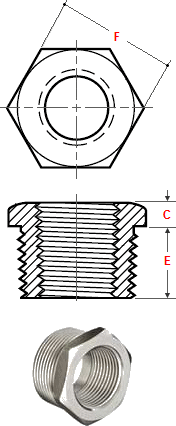
General notes..
- Dimensions are in millimeters unless otherwise indicated.
- Cautionary Note Regarding Hex Bushings..
Hex head bushings of one-size reduction should not be used in services where they might be subject to harmful loads and forces other than internal pressures.
Union (MSS SP-83)












